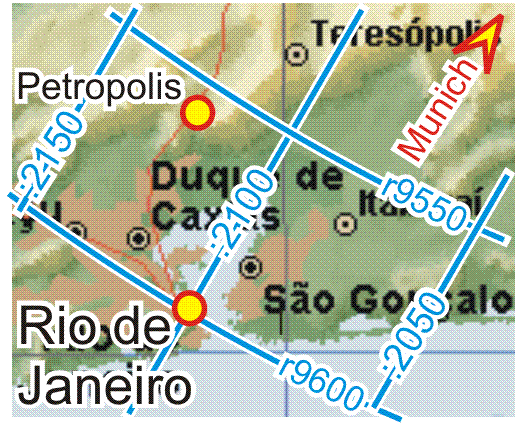
Within Rio, it is (will be) possible to find any target with easy brain work, that means
| - without maps, | - without names, |
| - without illogical numbers | - without arrows |
| - without floor marks | - without square grids |
| - without colors | - without compass or other navigation devices |
Buildings, crossings, metro stations, stop points, bridges, tunnels etc. have logical addresses like
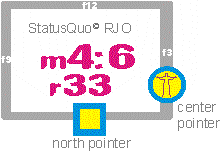
Arpoador StatusQuo© RJO m5:3
r48
Instituto Pereira Passos m1:15
r39
which are easy to understand if you associate the city with a clock as follows:
|
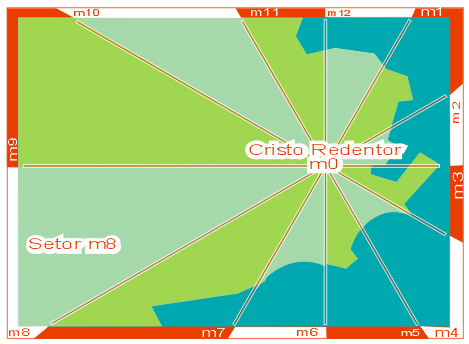
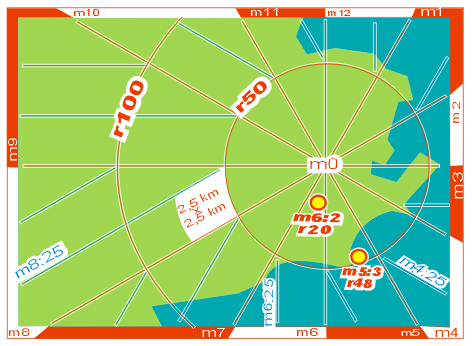
A relevant point as the Cristo Redentor was (will be) defined as a pole m0. Around this pole, the horizon is divided in 12 "horizon hours" m1 to m12 , whereas m12 points to north. This divides the city in 12 sectors. The picture signs the sector m8 as an example. |
 |
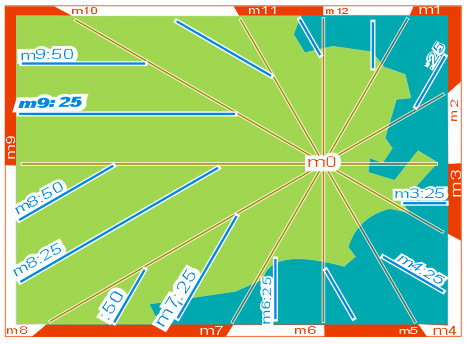 |
The sectors are divided in horizon minutes. These are not angles but DISTANCES to the horizon hour, in steps of approx one "block of houses", 100 yards or 100 meters. Example : m9:25 ( read "emm 9 point 25" or "emm nine 25" ). This is a line situated in a distance of 25 x 100m from the horizon hour m9, which points to sunset. The convention for horizon minutes is very simple: the greater, the later. |
|
Considering the distance to m0 as r = radius also in steps of blocks of houses, logical position codes for targets, buildings, crossings etc. come into existence, e. g. as shown on the picture: crossing StatusQuo© RJO m6:2 r20 In simple words: "r" is a numbering starting FROM m0, "m" is a north-direction-based numbering AROUND m0 and this simple methode covers a gigantic market gap: l o g i c a l and easy understandable p o s i t i o n codes. Example for a station code: Cardeal Arcoverde |
 |
|
|